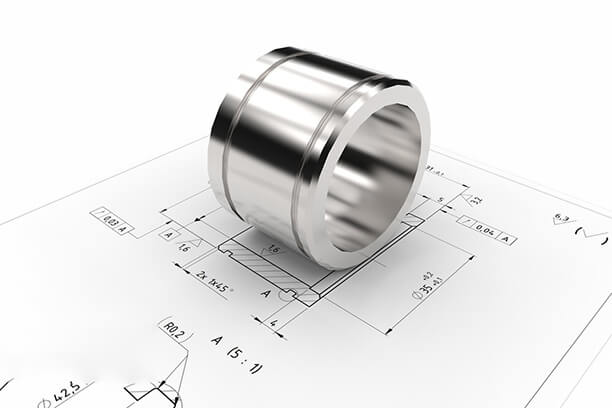
Explaining The Types Of CNC Machines & Their Categories
Upload Time:
Feb 23, 2024
Mastering the operation of each type of CNC machine significantly amplifies your efficiency. As you can imagine, this underscores the importance placed on learning to operate different types.It’s hard to put into words how much CNC machines have revolutionized machining operations. These machines offer versatility and flexibility allowing for processes and enhanced precision. However, it’s crucial to keep in mind that there are types of CNC machines to consider. To make a decision it’s important to understand the type you’re dealing with. This article aims to shed light on CNC machine varieties and their respective strengths.
What Are CNC Machines?
Unraveling the Mystery Behind CNC Machines
A computer numerical control (CNC) machine is an automated device designed for multifunctional processing tasks. These machines serve industries, Carrying out diverse functions, for CNC manufacturers. While their exceptional accuracy is widely recognized it’s worth highlighting some benefits of using CNC machine parts;
- Computerized Control: The notable feature of a CNC machine is its ability to be controlled by a central computer system. This computer interprets codes or programs that direct the machine’s movements.
- Versatility: We also mentioned earlier that CNC machines can handle a range of tasks. With various types of manufacturing machines available you simply need to select the one that suits your needs best.
- Automation: With CNC machines, there’s not much of a need for human intervention. Your job is to set the machine up and program it, and the machine does the rest. This structure ensures that you can cut down on errors as much as possible and optimize productivity.
- Repetition: As expected, CNC machines also do well when it comes to producing closely related or identical machine parts. For mass production, you can rest assured that any of the different types of CNC machines will easily come in handy.
At the end of the day, efficiency and precision are the goals of CNC machines. And, they help to achieve that seamlessly.
History & Evolution Of CNC Machines
Many people believe that John T. Parsons – a developer and inventor – was the man who led the way for CNC machines. The founder of Parsons Corporation in Traverse City, Michigan, Parsons collaborated with Frank L. Stulen – a former Air Force engineer – to create the first computer-based methods of solving machining problems in 1946.
The inventor secured a patent for a “Motor Controlled Apparatus for Positioning Machine Tool” by 1958. And as the 1970s dawned upon us, revolution characterized Army operations; it constructed and leased CNC computers to diverse manufacturers.
From that point forward, CNC machines advanced alongside other critical technological concepts; they propelled increased automation and productivity in various manufacturing processes.
Types Of CNC Machines
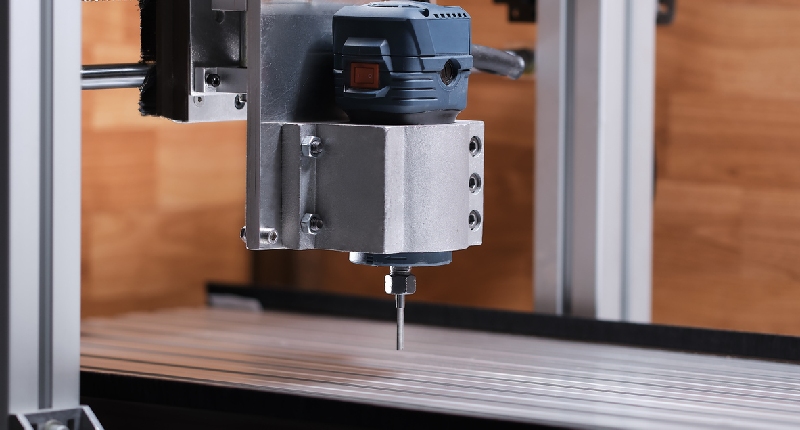

Now, let us delve into understanding the popularization process behind various types of manufacturing machines available:
CNC Milling Machines
Here, you have a computer-controlled tool, that primarily earns its renown for precisely cutting and shaping an array of materials. It operates efficiently without compromising performance even when confronted with multiple material options.
CNC milling machines utilize rotary cutting tools and operate in manufacturing and prototype development as well as diverse other tasks. They primarily aim to extract any surplus material from a workplace–a process that crafts the final component.
- Computer Control: The CNC milling machine typically uses a program in G-code for its operational instructions. Computer-controlled operation is standard practice today due to increased precision and efficiency.
- Versatile Operation: As earlier elucidated, CNC machines offer peak versatility; they facilitate the production of an extensive array of parts– varying in complexities, sizes and shapes. Moreover, they contribute to task management involving metal cutting, drilling, milling, and engraving among others.
-
Different Types Of Axes: When operating CNC mills and lathes, it is crucial to consider the configurations: three-axis or multi-axis. The machine options typically range from 3-axis, 4-axis, to 5-axis; ultimately determining the machine’s range of motion are these axis numbers – likewise shaping its capacity for producing complex shapes.
For instance, while 3-axis CNC-type machines can generally move in X, Y, and Z directions, 5-axis machines can do this while also accessing more angles by tilting and rotating the workpiece. - Workholding: A CNC milling machine will come with a worktable that helps to place a good hold on the workpiece. One can easily incorporate methods such as clamps, vises, and other special features to ensure a seamless hold.
- Tool Changes: The impressive ability to automatically change tools if necessary is at your disposal. You can utilize a variety of cutting tools – drills, end mills, and reamers for instance – within just one manufacturing operation thanks to this functionality.
- Today, across multiple industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medicine, CNC milling machines are ubiquitous. They assist in the production of both simple and complex parts, tailoring their output to your specific requirements.
CNC Turning Machines (Lathes)
- Primarily, the CNC turning machine concentrates on shaping and machining cylindrical materials. Its most prominent application, as implied by its name, involves a process where the operator rotates a workpiece; simultaneously applying a cutting tool to shape it into the desired form.
- CNC turning machines, as expected, operate in various fields. They can produce both small and large part batches, ensuring precision and consistency throughout production. These machines are primarily suited for the production of parts with rotational symmetry. Moreover, they excel at repetitive turning operations.
The CNC machining equipment boasts optimal precision and accuracy. It spares you from the repetitive handling of multiple tasks and achieves this by incorporating several features, namely:
- Use With Cylindrical Workpieces: Most CNC turning machines undergo impeccable calibration to operate with cylindrical workpieces; however, they are not limited exclusively to this type of piece. The performance may vary when working with other forms – it’s just that the outcomes tend towards superior quality for cylindrical components.
- Dual-Axis: Generally, CNC turning machines operate as either single-axis or multi-axis. The cutting tool on a single-axis lathe moves along the length of the workpiece; however, with multi-axis options–it’s an entirely different scenario. These innovative tools offer not only additional rotational movement but also angular movements by moving in radial directions.
- Tool Changes: CNC turning machines primarily offer the advantage of accommodating various cutting tools, thereby enhancing versatility. This is due to their ability for tool changes.
- Workholding: The methods for securing workpieces with CNC turning machines include collets, chunks, and fixtures.
Advantages Of CNC Turning Machines
CNC Turning Machines hold several advantages:
- Specializing in cylindrical machining, which significantly enhances the production of your cylindrical components; this stands as a major benefit they offer.
- With all types of metal CNC machines, you get optimal precision and efficiency.
- In most cases, the machines work with single-setup operations. This eliminates the need for diverse machining steps
- CNC turning, a chip-producing operation in material processing, actively minimizes waste.
CNC Plasma Cutting Machines
One of the most intricate material formation processes is plasma cutting. It enables us to shape metals into familiar forms, making it a versatile process capable of serving multiple functions.
CNC machining equipment, on the other hand, significantly enhances the traditional plasma-cutting process. A CNC plasma cutter harnesses a high-temperature plasma arc; this machine offers versatility in operation across various material options.
The following features and characteristics are available to you with a CNC plasma cutter:
High-Temperature Plasma Arc: The CNC plasma cutter’s primary component, the arc originates from ionizing a gas, passed through its nozzle.
The arc, generating an ample amount of heat, melts the metal. Simultaneously, a high-velocity jet of ionized gas forcefully blows away the molten material; ultimately resulting in a clean cut.
Operational Versatility: If you have a metal material requiring CNC machines for metal cutting, a CNC plasma cutter offers the necessary operational versatility to process it.
Speed and Precision: To be fair, the CNC plasma cutter exhibits a slight precision lag. Nevertheless, with the incorporation of advanced torches and tools, it still yields substantial accuracy.
Combined with the machine’s impressive speed, this feature locks it for various manufacturing processes.
CNC Nesting: The software that directs a CNC plasma cutter’s operations typically possesses nesting capabilities. These features — by strategically arranging parts on the raw material sheet — enhance efficiency and reduce waste.
The Principles Of CNC Plasma Machines
Every CNC plasma cutter operates based on the principles of electrically conductive gas. This gas is made to pass through a nozzle, creating a plasma arc that easily melts and slices through the metal.
For that process to go without a hitch, several steps are required:
Gas Supply
You’ll find that the first step in the overall process involves providing a suitable amount of a gas – or perhaps even a mixture of gases. In most cutting processes, the gases used are nitrogen and oxygen – and, in some cases, you can find compressed air being used. As long as the gas choice is compatible with the material, you shouldn’t have a problem.
Plasma Torch
At the very heart of the plasma cutting machine, you have a plasma torch. Different components accompany this torch:
- An electrode is typically crafted from a refractory material and carries a negative charge.
- A nozzle surrounds the electrode that facilitates the flow of gas.
- The workpiece and the electrode establish an electrical circuit. This circuit, in turn, generates a spark. This spark ionizes the gas – transforming it into a plasma arc.
Formation of the Plasma Arc
An electrically conductive gas generates the plasma arc as it passes through the nozzle. When heat applies to this phenomenon, temperatures of up to 30,000 degrees Fahrenheit (16,650 degrees Celsius) can be achieved.
Cutting the Materials
From there, the plasma arc is directed towards the material. Applying heat allows the metal to melt; simultaneously, a high-velocity jet of ionized gas blows away molten metal – thus yielding a precise cut.
CNC Control
As you’d expect, the implementation of a CNC system guides the entire process. The system interprets the part program and transmits instructions for all critical parameters; thus, with its help, the cutting torch crafts precise product profiles.
The Control of the Z-axis
The CNC plasma cutting machine also loads a Z-axis control feature. This enables the torch to sustain an optimal and unvarying distance from the workplace during your cuts.
Automated Process
Set up the machine and load the part program. Then, you can initiate a self-operating cutting process. The program’s specific instructions guarantee efficiency during the cut, thereby providing assurance in its operation.
Taking Out the Slag
Once you finish the process, it is perfectly normal to observe some residual slag at the cut edge; however, utilizing post-cutting methods such as grinding allows for a complete removal of this slag.
Known for its efficiency, speed, and versatility in cutting a broad spectrum of metals, the CNC plasma cutting process proves particularly valuable in industries that prioritize metal-cutting operations: metal fabrication; construction; and automotive manufacturing. The CNC control guarantees consistent and unwavering results, thus earning it status as the preferred method for high-precision tasks involving cutting.
CNC Laser Cutting Machines
Next, we look into the CNC laser cutting machine: a powerhouse that harnesses the advantages of CNC automation in traditional laser cutting. This strong tool engraves and cuts an extensive variety of materials with astounding precision, making it easy to manipulate the material.
Here are some of the crucial components of a CNC laser-cutting machine:
- The Primary Laser Source: Functioning as the heart of the CNC laser cutting machine, this source generates a high-intensity laser beam: which is instrumental in delivering precise cutting action.
- Laser Optics: Focusing and directing the beam itself is what the laser optics do. They make the process smooth and can work as long as you calibrate and align them correctly.
- Z-axis Control: You can control the working distance between the laser cutting head and the workpiece effectively with Z-axis control. This control guarantees consistent focus and appropriate alignment parameters.
- Nozzle & Gas Delivery System: If you are cutting metal, an assist gas delivery system is necessary to augment the process. The system feeds nitrogen or oxygen into a delivery system in the nozzle, while a nozzle directs this air toward your workpiece and effectively clears away any debris.
- Coolants: Some laser cutting machines may feature coolant systems for dissipating the heat generated during the process; this is part of their Dust Collection.
- Fume Extraction System: Should the cutting process generate excessive fumes, you might need to implement a fume extraction system. Its function involves removing and filtering these produced emissions.
CNC Router Machine
For the next option, we have CNC router machines. In most instances, these devices help to shape and engrave different materials, working with a versatile material set to achieve the right results.
For CNC router machines, you have the following major components:
- Available Axes: Most CNC routers operate along the three main axes. X and Y control more horizontal movements, while vertical movement is denoted by the Z axis. But, you should also remember that some advanced routers come with more rotational axes to handle complex routing tasks.
- Spindle or Router Bit: The router bit is the major too that handles cutting. With high-speed rotation, it is responsible for carving, cutting, and material engraving. You can also choose different bit types based on the material you’re working with.
- Motion System: The router’s movement is achieved by combining different drives, motors, and linear guides. These components collaborate to dynamically position the moving router bit.
- Dust Collection System: The cutting process inevitably accumulates debris: however, a dust collection system mitigates this issue. Not only does it protect the machine; but also ensures an immaculate working environment is maintained.
CNC Electrical Discharge Machine (EDM)
The CNC Electrical Discharge Machine (EDM) is a sophisticated tool that utilizes computer numerical control to guide electrical discharges for precise machining operations.
For a more efficient removal of materials from a workpiece, consider the CNC EDM. This machine primarily targets conductive materials such as metals; it operates by manipulating a controlled electrical spark between its electrode and the material.
The intricate process of the EDM guarantees precise and intricate machining. This proves particularly vital in industries that necessitate complex shapes.
Typically, two types of CNC EDMs are available:
- Wire EDMs: In the wire EDM, a thin wire–electrically conductive in nature–serves the purpose of cutting through the material. The wire is guided along a predetermined path, with controlled electrical discharges removing the excess material from the workpiece.
- Sinker EDM: Also known as a Ram EDM, the sinker EDM uses an electrode with a special shape – usually made with copper or graphite. The electrode is lowered into the workpiece, creating holes and cavities. From there, both the electrode and the workpiece are dropped into a dielectric fluid, where controlled sparks act on the workpiece and you achieve your desired shape.
CNC Waterjet Cutting Machine
Today, waterjet cutting is a leading material-cutting process. Concurrently, CNC machining enhances its overall efficiency; an invaluable contribution in this dynamic industrial landscape.
High-pressure water streams and abrasive materials in these machines facilitate precise cuts across a diverse array of materials. The computer-based control systems not only accomplish precision effortlessly but also penetrate through complex materials with ease.
CNC waterjet cutting machines, in general, yield several advantages over alternative waterjet cutting methods; these encompass:
- Heat-Affected Zones: CNC waterjet cutting machines have garnered immense popularity due to their utilization of heat-affected zones: this is primarily attributed to the advantageous nature these zones provide when manipulating materials sensitive to high temperatures.
- Environmental Sustainability: The CNC waterjet cutting operation is also known for its eco-friendliness since it eliminates the production of any dangerous fumes. Moreover, recycling is an option for the water employed in this cutting process; thus rendering it not only environmentally advantageous but also sustainable.
- Accuracy: Of course, you also get a significant amount of accuracy from CNC waterjet cutting. When you need tight tolerances, the process works perfectly for you.
Conclusion
Mastering the operation of each type of CNC machine significantly amplifies your efficiency. As you can imagine, this underscores the importance placed on learning to operate different types.
Dedasun stands ready to connect you with the precise CNC machines you require; contact us today. Allow our expertise to assist you – we are here for your needs.
Relevant News